What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free software from Google that allows you to add different types of tags to your website. Popular examples include Google Analytics tracking code, Google Analytics events, Google Ads conversions and Google Ads remarketing tags. In addition to Google products, it is possible to add a number of different codes to a page using the Tag Manager.

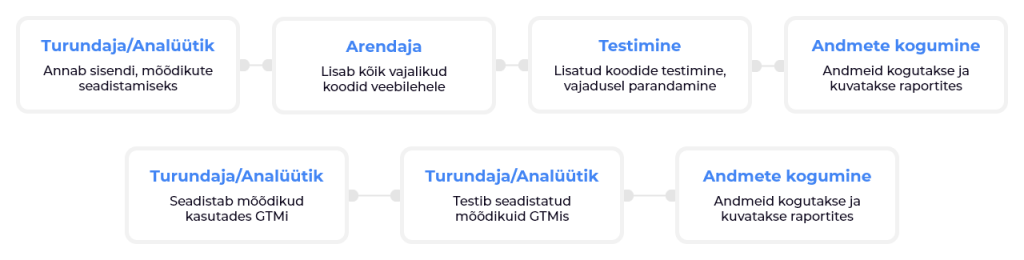
More effective results with lower development costs
Without Google Tag Manager, all Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, Hotjar, etc. codes would have to be added to each site manually by the Developer. If there is a lot of code to be added, this is a time consuming task, plus if the code needs to be updated, the whole process needs to be redone (for example Google Analytics updated to Google Analytics 4). When using Google Tag Manager, it is necessary to involve the Developer in the initial setup – adding a Tag Manager script to the page and an additional module if required. Further configuration and administration can be handled by the Marketer.
Which means that if you would normally need to contact a Developer to set up, say, Google Ads dynamic remarketing, who would add all the necessary code to the page, you would then need to test that all the attributes are getting into Ads in the right form, and if there are any problems, shuttle back and forth between Developer and Marketing to get the tag working. By using Google Tag Manager, Marketing can take the configuration they need for Tag Manager from Google Ads, add it to Tag Manager and test directly in Tag Manager that all attributes are correct and change them instantly. This workflow makes it quicker and easier to add new tags to the page.
Reduce page loading time
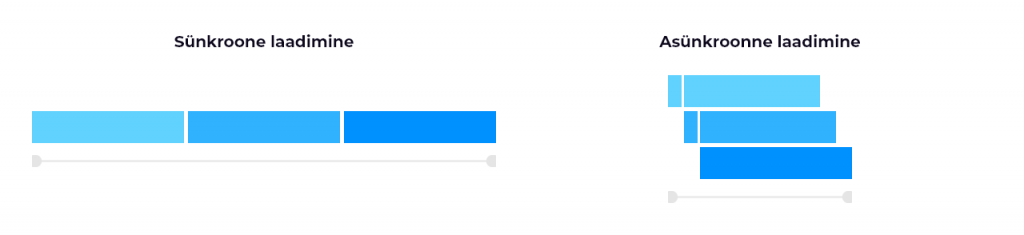
Adding different tracking codes directly to a page loads them synchronously, even if they are not needed immediately, and this can make a website slow. If one code takes longer to load it will slow down the loading of all subsequent codes that come after it. The slower the web page, the greater the chance that the user will leave the page without making a purchase.
Tags created in Google Tag Manager are loaded asynchronously by default, which means that each tag is started when it is ready to be started. In addition, the Tag Manager itself can control the order in which tags are launched using tag ordering and launch priority.
Google Tag Manager and iOS 14.5 updates
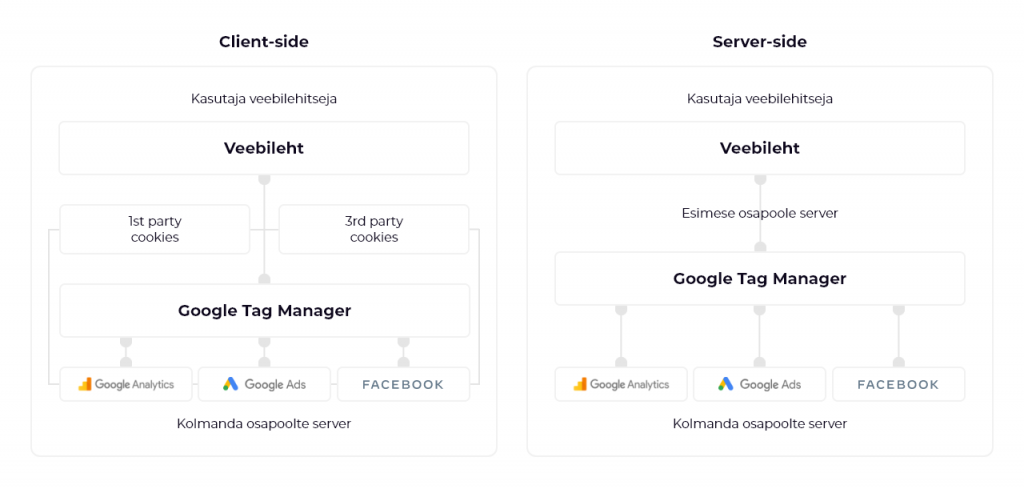
Facebook, LinkedIn, Google and others use 3rd party cookies to collect analytics. Google Tag Manager itself does not store data, but is a data broker between platforms, there are no changes to the way Tag Manager works with the iOS 14.5 changes. However, it is wise to prepare for the iOS 14.5 changes today, as Chrome browser will also remove all 3rd party cookies in 2022. One solution is to use server-side collection of analytics.
Why think about server-side tracking?
In addition to browser-based analytics collection, Tag Manager added server-side tracking last August. Server-side analytics collection reduces the problems caused by the browser. For example, last year there was an issue where security was enhanced with browser updates and the user session was terminated when proceeding to the payment environment and a new session was started when returning to the e-store from the bank. This problem caused a lot of havoc in Google Analytics, where orders did not make it into reports. With server-side tracking, the data is not passed on based on browser information, but from the e-commerce system administration, i.e. when the order reaches the administration of Magento, Shopify, etc., the information is sent directly to the third-party analytics – Google, Facebook, etc.
Server-side analytics collection also means that competitors don’t get information about your digital marketing and metrics. Today, it is very easy with different browser extensions to see exactly what information a merchant collects about its visitors – custom dimensions, custom metrics, what goals are set, conversions, enhanced ecommerce presence. Certainly every website should have a privacy policy describing what data is collected and for what purpose, but server-side data collection does not give a competitor the advantage of seeing your specific ecommerce metrics.
Since server-side tracking completely removes all third-party code from the page, it improves page load time even more than simply using Tag Manager, increases the security of customer data and gives control over data flow. In a recent Deloitte study, it was found that reducing mobile website load times improved purchase journey progression for all brands surveyed. In e-commerce, a 0.1 second change in website load time increased the number of orders by 8.4%, the average order amount increased by 9.2% and the product card bounce rate decreased by 5.4%.
The initial setup of server-side data collection is more time-consuming than setting up a browser-based Google Tag Manager, but is time-saving in the long run, saving time debugging new browser versions and when implementing compliance with new privacy laws.
The main Google Tag Manager tags
The Tag Manager is mainly used for exchanging data between Google products. For example, to configure Google Analytics base code and enhanced e-commerce. In order to create enhanced e-commerce reports in Analytics, Product Impression, Product Click, Product Detail, Add to Cart, Remove from Cart, Checkout, Checkout Option, Purchase, Refund, Promotion View and Promotion Click tags need to be added to the page. The other popular ones are Google Ads Remarketing and Conversion tags. In addition, e-stores often have a visual analytics tool such as Hotjar, Clarity or CrazyEgg set up. Using three different analytics tools, a page can have 15-25 different scripts.
If you feel Google Tag Manager could help your e-business to grow then contact us!